Skip to main content
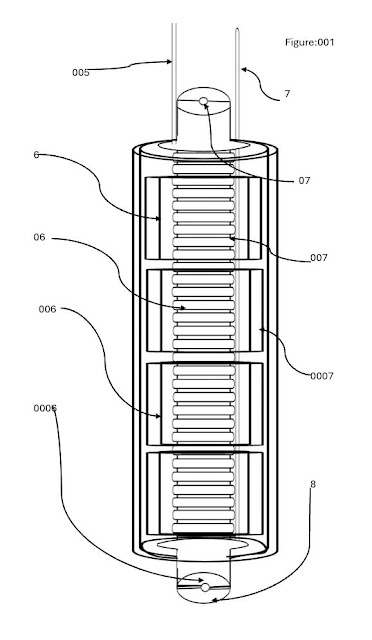
patent application / JERMAINE MORTON invention: 🧾 Provisional Patent / Technical Whitepaper Title:GEM-HORN Electrodynamic Light-Emitting Horn Sensor for Subsurface Diamond Detection Abstract The invention relates to a battery-powered, portable diamond detection device utilizing a combined electrodynamic, optical, and acoustic scanning system embedded within a long-rod sensor probe. The device emits high-frequency electromagnetic pulses and infrared light into the ground and measures the resulting reflectivity, conductivity, and vibrational feedback from subsurface materials. Through spectral and vibrational pattern matching, the system identifies unique diamond signatures, enabling non-invasive, touchless ground terrain scanning. The device is optimized for use in mining, security, and geological surveying applications, allowing rapid identification of buried diamonds in natural or artificial environments. Technical Summary The proposed system consists of the following subsystems integrated into a rod-shaped handheld probe: 1. Power Source Rechargeable 12V lithium-ion battery pack Supplies voltage to all active components via regulated buck converters 2. Electromagnetic Induction Subsystem A copper coil wrapped along the probe shaft Driven by a pulse-width modulated H-bridge MOSFET circuit Emits controlled electromagnetic pulses into the ground Measures back-induction using a return detection circuit to identify dense or resistive structures 3. Light Emitting Horn Assembly Infrared laser emitter (830–1064 nm) positioned at the horn tip Emits directed IR pulses downward into terrain IR photodiode array receives reflected spectra Spectral signal processed and compared to diamond IR absorption signature 4. Acoustic Sensor System Sonic pulser (ultrasonic or piezoelectric) injects high-frequency acoustic waves Echo return read by sensor Differentiates reflective profiles between crystalline vs non-crystalline materials 5. Signal Processing Unit ESP32 microcontroller handles sensor inputs, timing, and signal correlation FFT and pattern-matching algorithms identify diamond-like responses OLED screen and audio/visual feedback (LED, buzzer) inform user 6. User Interface & Alert System OLED screen shows status and detection readouts Buzzer or speaker emits audio tone upon positive detection RGB LEDs for color-coded visual alerts Optional wireless connection to mobile app for data logging Claims An integrated, battery-powered, portable device for underground diamond detection comprising: an electromagnetic pulser coil, an infrared laser emitter, a photodiode-based optical return sensor, and an acoustic vibrational transducer, wherein the combination of electromagnetic, optical, and acoustic data is used to determine the presence of diamond material beneath the surface. A diamond detection method using an electrodynamic rod-shaped scanning device that emits pulsed infrared radiation and electromagnetic waves into a terrestrial surface and analyzes return signals via a microcontroller. A long rod-shaped horn sensor with an integrated laser array and detection circuit embedded at the tip, capable of spectral fingerprinting subsurface materials without physical contact. A touchless terrain scanning system, wherein proximity to buried gemstones is determined based on return signatures of heat, light, and magnetic field distortion. An electromechanical horn assembly comprising a focused emitter array, vibration sensors, and a spectral return processor configured to differentiate diamonds from other subterranean minerals or objects. Drawings/Diagrams (Descriptive references) Figure 1 – System schematic showing battery pack, voltage regulators, ESP32 microcontroller, EM coil, H-bridge driver, IR laser module, and sensor return paths. Figure 2 – Side view of the long rod design with horn-shaped emitter at the tip, sensors embedded around emitter, handle-mounted display, and internal wiring channel. Figure 3 – Signal flow diagram showing pulse emission, terrain interaction, return detection, and classification. Figure 4 – Comparative IR and EM return signal profiles: diamond vs quartz vs zircon. (Illustrations can be manually drafted based on these descriptions or rendered using CAD tools.) Applications 1. Mining Operations In-field diamond identification without excavation Rapid surveying of rock faces, soil, and caves 2. Security and Customs Non-invasive scanning of packages, containers, or hidden compartments Detects concealed or embedded gemstones 3. Geological Research Assists geologists in tracking kimberlite or carbon-rich mineral zones Enhances field efficiency in sample targeting and mapping 4. Exploration & Archaeology Useful for exploration teams searching for natural deposits Detects high-refractive carbon-based materials in ancient burial or ceremonial sites subject not limiting to additional system or structure potentiometric range design inventor Jermaine Morton










































Comments
Post a Comment